MDCAT Biology – Chap#2 Bio-energetic
The study of conversion of energy from one form to another form and its utilization by living organisms is called Bioenergetics.
Cellular Respiration (Catabolic Process):
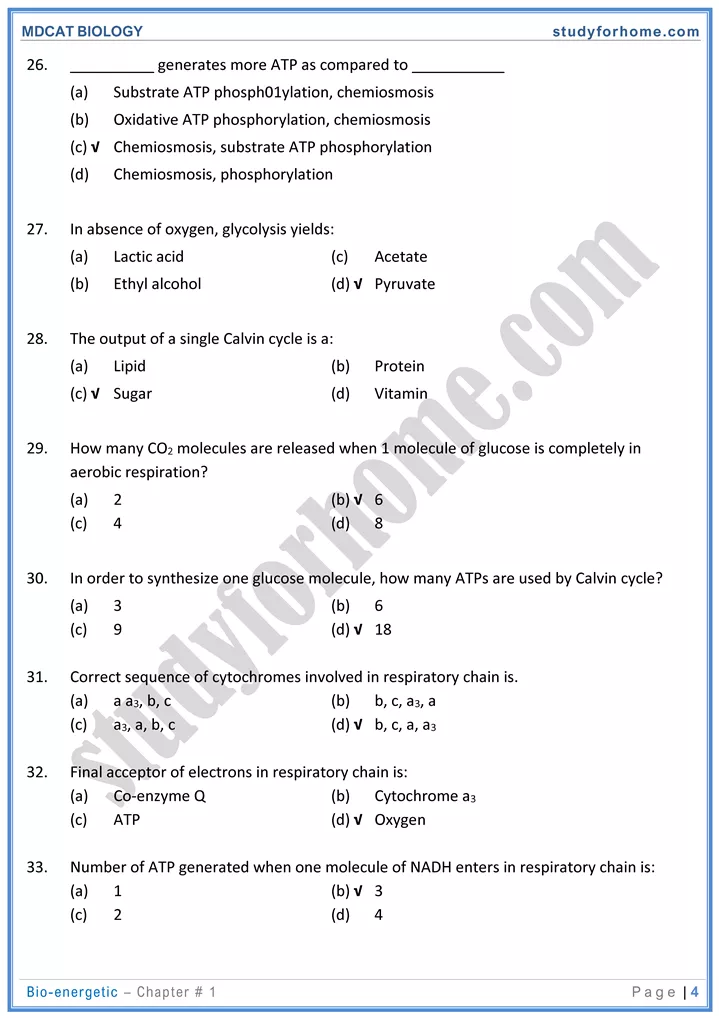
Glycolysis
- It occurs in both living plant and animal cells.
- Glyycolysis does not need atmospheric oxygen and can proceed in its absence as well as in presence.
- In glycolysis a molecule of glucose (6-C) is broken down into two molecules of pyruvic acid (3-C).
- End products of glycolysis: 2 molecules of pyruvic acid and two molecules of NADH.
Kreb’s Cycle ( Citric acid cycle or Tri carboxylic acid Cycle):
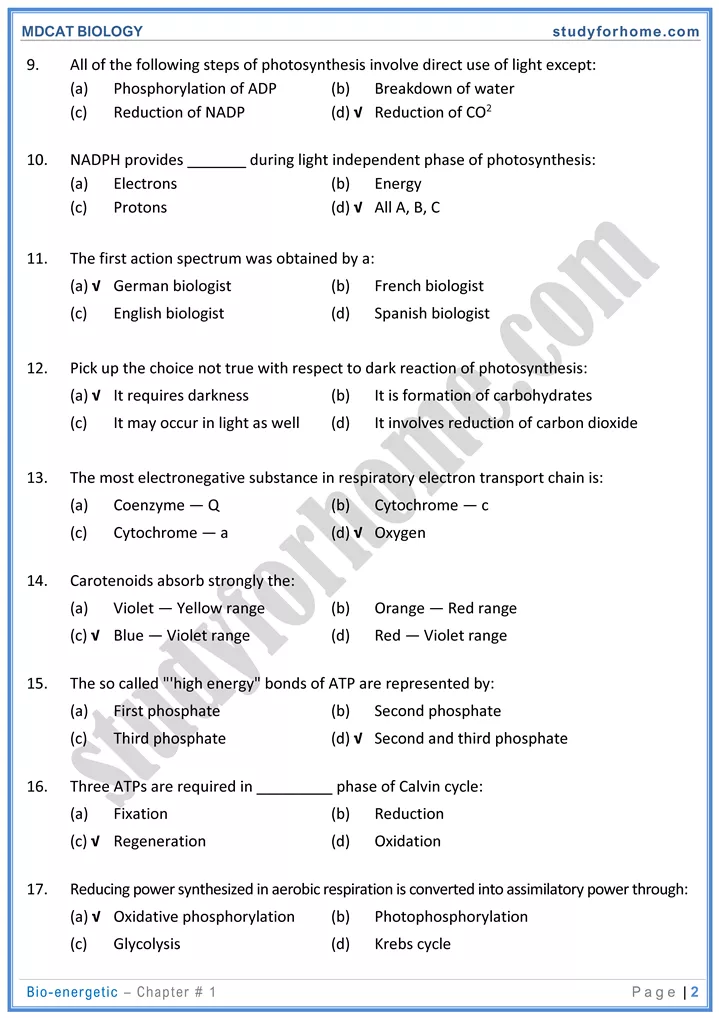
- Reactions of Krebs cycle take place in the matrix of mitochondria and can proceed only in presence of atmospheric oxygen.
- During reactions of Kreb’s cycle, hydrogen atoms in pairs are extracted from substrates.
- NAD+ and FAD+ act as hydrogen acceptors (carriers) and carry 2H+ + 2e to electron transport system.
- During Kreb’s cycle at one step, one molecule of ATP is formed by substrate level phosphorylation
Electron Transport System of Mitochondria
- Electron transport system is located in the inner membranes (Cristae) of mitochondria.
- The ETS consists of a series of iron containing proteins called cytochromes and coenzymes. The cytochromes include cytochromes ‘b’, cytochrome ‘c’, cytochrome d’ and cytochrome ‘Q3’ arranged in sequence. The co-enzymes are NAD and FAD.
- Final electron acceptor is atmospheric oxygen which also picks up protons (H+) and forms water.
Oxidative Phosphorylation:
- When the energy for synthesis of ATP is provided by oxidation of nutrients, the process is called oxidative phosphorylation.
- In cellular respiration 36 ATF are formed out of which 32 A TP are formed by oxidative phosphorylation in electron transport chain.
- Substrate level phosphorylation: It is the production of ATP by the direct transfer of a high energy phosphate group that does not involve electron transport or chemiosmosis.
- 4 ATP out of a total yield of 36 ATP per glucose molecule are produced by substrate level phosphorylation.
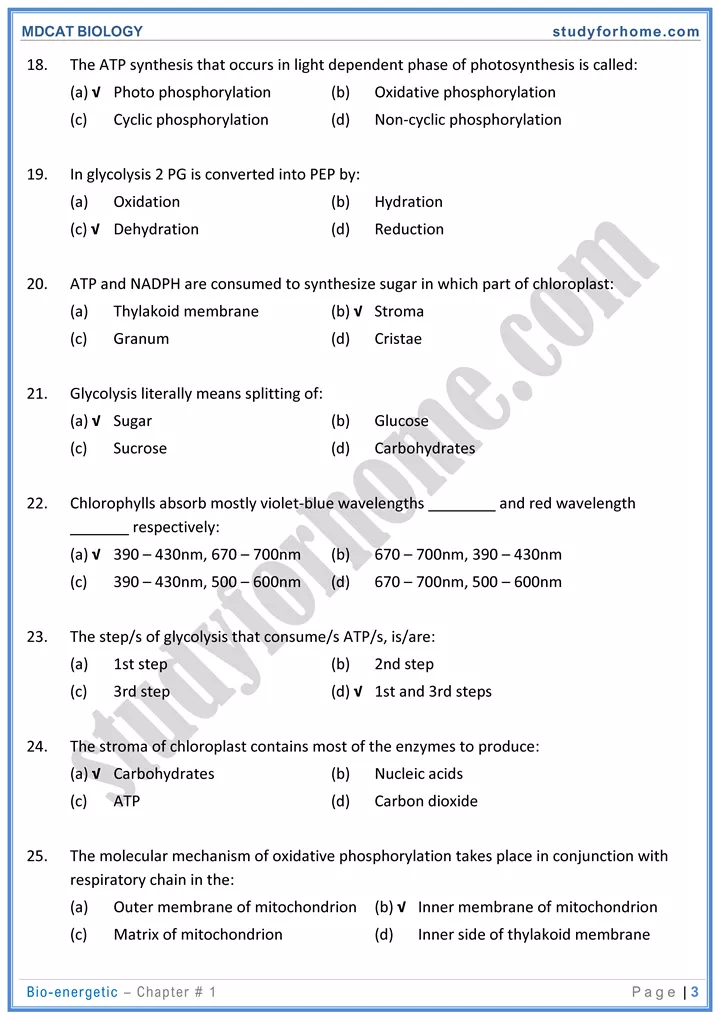
Photosynthesis (Anabolic process):
- Conversion of light energy to chemical energy of organic compound (starch usually).
- Red and blue are most effective wavelengths for photosynthesis.
(i) Light dependent reactions occur in thylakoids.
- Light energy is converted into energy carrier molecules ATP and NADH.
- ATP and NADH are ends products of light reaction.
(a) Photophosphorylation is the process of formation oi ATP using energy of light during light reactions. ETS of chloroplast is involved in this process.
(b) Non-cyclic photophosohorylation is so called because excited electrons do not return back to the original donor. Flow of electrons is from water to NADP through PSI! & PSI. PSII & PSI are needed. End products are ATP and NADH. Path of electrons is water → PSII → Phaeophytin → plastoquinone → cytochrome complex → plastocyanin → PS-I → Ferridoxin → NADP+
(c) Cyclic phosohorviation is so called because the excited electrons are finally returned back to the original donor PS-I.PS-l is needed only & the end product is ATP. The path of electron flow is PS-I (P-700) → primary acceptor → ferredoxin → cytochrome complex → plastocyanin → P-700 (PS-I)
(ii) Calvin Benson Cycle (light independent / dark reactions)
- It doesn’t not require light energy and can proceed in light as well as in dark.
- Energy is provided by ATP and NADH.
- It occurs in stroma. Calvin cycle consists of 13 main reaction which use 11 enzymes.
Carboxylation (carbon fixation) occurs by combination of CO2 molecule with a 5- carbon sugar called ribulose bisphosphate (RuBP). Enzyme required for this is RuBP carboxylase / oxygenase (Rubisco), which is the most abundant enzyme and protein on this earth.
First stable intermediate compound (detectable molecule of photosynthesis) is phophoglycerate.
The primary end product (first sugar formed) ts 3-hosphoglyçeraIdehyde (PGAL.) or triose phosphate.
C3 plants fix CO2 to a 5—C compound RuBP which acts as CO2 acceptor. In C4 plants, CO2 is (fixed to a 4c compound called oxaloacetate). Important C4 plants are members of grass family such as corn and sugar cane
SOME IMPORTANT TERMS:
Trophic level: Position of an organism in the food chain is called its trophic level.
Food chain: A series of organisms through which energy flows in an ecosystem is called food chain.
Pyramid of energy is a diagrammatic representation of available energy at each trophic level.
Productivity and ecosystem is the rate at which new organic molecules are formed in an ecosystem.
Primary productivity is the rate at which energy is captured and stored in food molecules by producers.
Gross primary productivity is the rate at which the total solar energy is converted to chemical energy of the food matter synthesized by the producer.
Net primary productivity is the amount of energy stored in the producers and is available for use by the consumers.
Secondary productivity is the rate of production of new organic matter by consumers (herbivores, carnivores and detritivores).
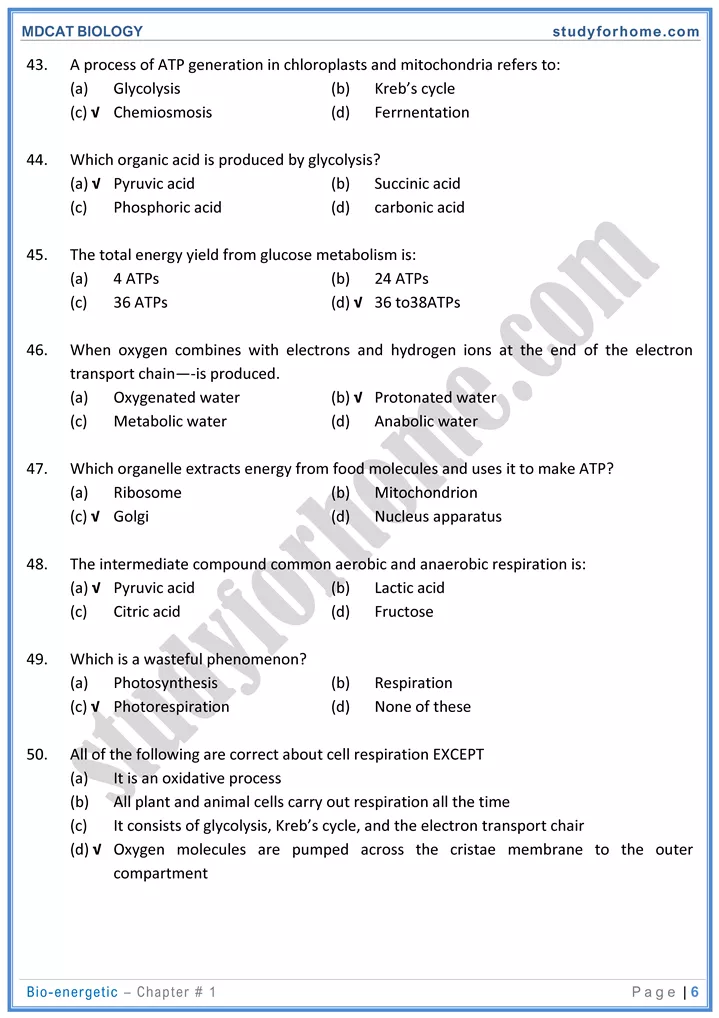
Respiratory Diseases:
1. Pulmonary Carcinoma (Lung Cancer
2. Emphysema
3. Asthma
4. Tuberculosis