Diversity among Animals – Chap 6 – Biology MDCAT
Introduction
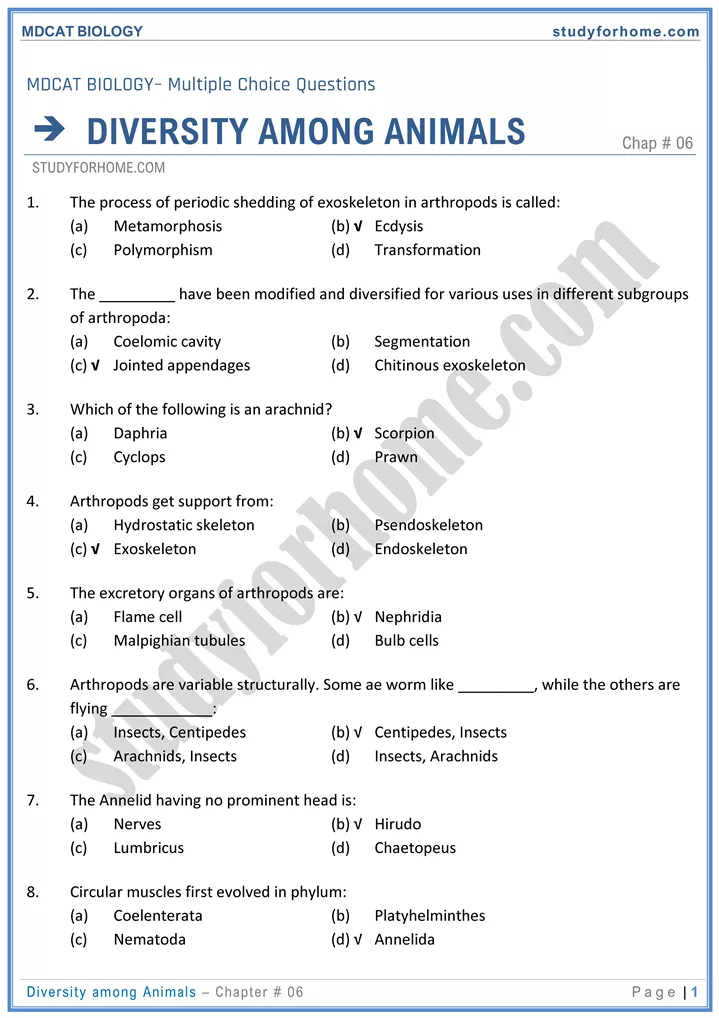
- Cavity formed by splitting of mesoderm and is lined by mesoderm is called coelom.
- Animals having coelom are coelomates. E.g. animals form annelids to chordate
- Coelenterates / cnidirians are primarily radially symmetrical whereas echinoderm mates are secondarily radially symmetrical.
- Platyhelminthes and Aschelminthes (nematodedes) are tnploblastic but are not coelomates. i.e. Acoelomates and pseudocoelomales respectively.
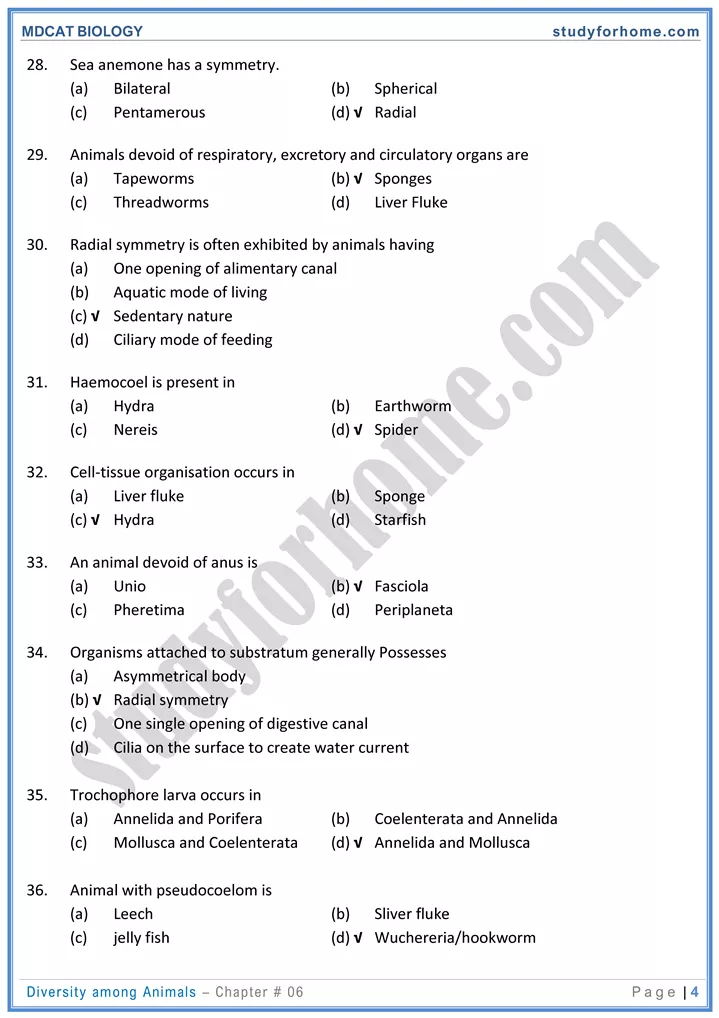
- Phylum Porifera (Sponges):
- Tissue and organs are absent. Most primitive animals.
- Canal system is present. Ostiaare incurrent and oscula are ex-current pores.
- E.g. Ascon, spongilla (freshwater), Sycon, Bathsponge.
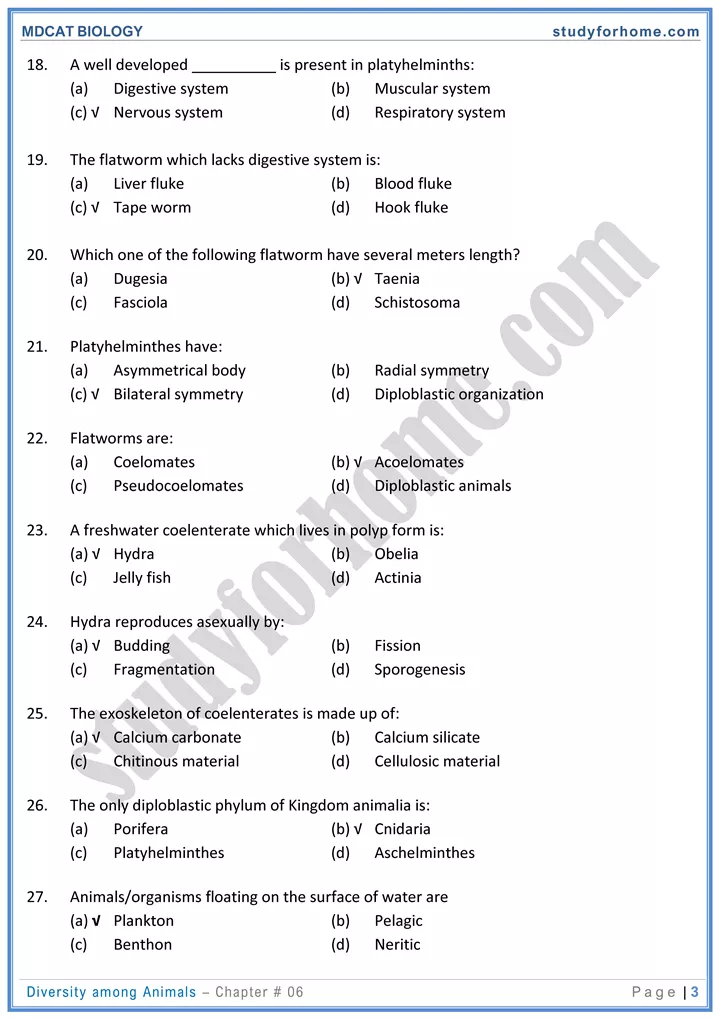
- Phylum Cnidiria (Coelenterata)
- Organs absent. Tissue grade of organization.
- Cnidocytes are cells containing stinging capsules called nematocysts.
- Neurons form a nerve net.
- Polymorphism. Physaha is a polymorphic colony having 3 types of zooids.
- Alternation of generations takes place between asexual (polyp) stage and sexual (medusa) stage.
- E.g. hydra. sea anemone, corals are palyps. Physalia, jellyfish are medusa.
- Phylum Platyhelinthes
- Dorsoventrally flattened.
- Protonephridia (flame cells) are excretory organs.
- Tape worm (Taenia) is digenic having human and either pig or cattle as hosts. Liver fluke (fasciola hepatica) is also a digenic parasite having hosts cattle and water snail.
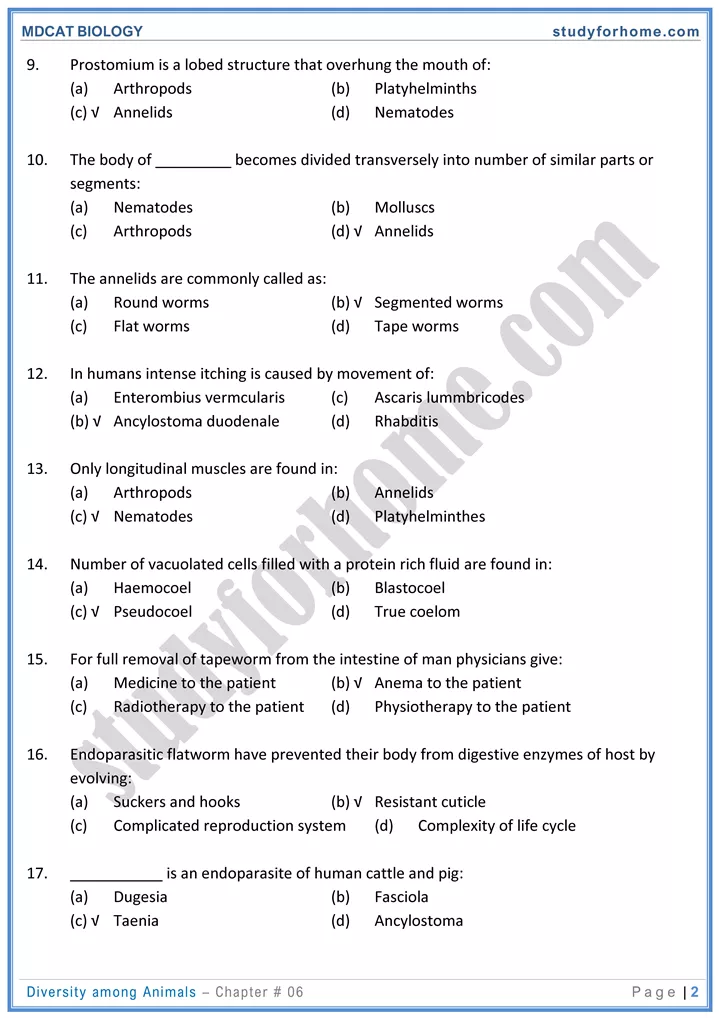
- Phylum Nemathelminthes (Nematoda- Round worms):
- Sexes are separate. Sexually dimorphic.
- Alimentary canal with mouth and anus.
- Almost all members are parasites.
- E.g. ascaris. hook worms, filanal worms. thread worms etc.
- Phylum Annelida (Segmented worms):
- Metamerically segmented. Setae are present on parapodin in neries. Leech is without setae whereas in earthworm it is directly attached to body wall.
- Blood vascular system is closed type. Hemoglobin is freely present in plasma,
- Nereis is unisexual and marine.
- Earthworm and leech are hermaphrodite.
- Phylum Arthropoda (Jointed legs):
- The Largest phylum. 80% of all known species belong to this phylum.
- Chitinious exoskeleton is present. Open type blood vascular svstem. Body cavity is called haemocoel. Containing color less blood called haemolymph Hb absent.
- Class insecta have three pairs of walking legs. Apterygota or pterygota are two groups of this class.
- Class crustacea have 5 pairs of legs. e.g. crabs, prawns, lobsters. Sacculina is parasite.
- Merostomata are marine, mouth is surrounded by plates. Limulus (king crab) is considered as living fossil.
- Arachnida have 4 pairs of legs, poisonous. antennae are absent. Silk glands are present in spider, secrete silk threads to form nests and webs. Include scorpions, ticks, mites, etc.
- Myriapoda have many pairs of walking legs. e.g. centipedes and millipedes.
- Phylum Mollusca (Soft bodied) Unsegmented:
- Mantle is glandular membranous covering which secretes shell.
- Single ventral muscular foot present which is modified in sepia and octopus as oral arms.
- Nautilus has external shell, sepia and squids have internal shell. Octopus has no shell.
- Pila and other snails are asymmetrical due to torsion. Unia and oysters have bivalve shells.
- Ranula is a rasping tongue like structure with horny teeth in many molluscs.
- Phylum Echinodrmata (Spiny Skinned):
- Larva Bipinnaria is bilaterally symmetrical.
- Exclusively marine. Water vascular system is present. Tube feet are part of water vascular system and are also used in locomotion.
- Skeleton of hard calcareous plates and spines is present.
Phylum Chordata:
- Class Pisces.
- Gills, paired fins and dermal scales are present.
- Single circuit circulation.
- Osteichthyes are bony fishes having terminal mouth and operculum; Ctenoid I cycloid scales are present. e.g. Eel, sea horse, flying fish, etc.
- Chondirichthyes are cartilaginous fishes having ventral mouth and placoid scales.
- Includes marine fishes like sharks and rays, etc.
- Torpedo is an electric ray.
- A small group of bony fishes having gills and lungs is known as dipnoi (lung fishes).
- Protopterus is an African lung fish.
- Class Amphibia:
- Evolved from lobe finned fishes (Rhipidistian).
- Respiratory skin, exoskeleton is absent.
- In Caecilians pentadactyl limbs are absent.
- Digits are without claws.
- Heart is 3 chambered. Double circuit circulation.
- E.g. frogs and toads are tailless, salamanders are lizard like tailed amphibians. Blind worms (Caecilians) are legless amphibians.
- Class Reptilia:
- Pendactyl limbs are present having digits with claws. Snakes are legless.
- Respiration is exclusively terrestrial takes place by lungs.
- Heart is incompletely four cnambered except crocodile.
- Exoskeleton consists of epidermal scales. Bony shell or scales may also be present.
- Class Aves (Birds):
- Birds are glorified reptiles.
- Lungs and air sacs present. Syrinx is voice box.
- Many bones are pneumatic and have air spaces.
- Exoskeleton consists of feathers. Scales present on legs.
- Wings are modified forelimbs. Beak without teeth is present.
- Ratitaeare running birds having sternum without keel. e.g. kiwi, Ostrich, emu, Cassowary, etc.
- Carinatae are flying birds having sternum with keel e.g. sparrows, crow, etc.
- Class Mammalia:
- Mammary glands, hair, sweat and sebaceous glands are present.
- Pinna or external ear is present, except in prototheria.
- Important Definition
- Non nucleated RBCs are present.
- Hairs are limited to whiskers in whales and dolphins.
- All are viviparous except prototheria.
- Prototheria are egg laying mammals e.g. echidna and duck bill platypus.
- Metatheria are pouched mammals e.g. wombats, kangaroo, opossums, koala bears.
- Eutheria: The fetus is nourished from the blood of mother via placenta. e.g. hedgehog horse, lions, whale, bats. etc.
- Markhor (wild goat) is national animal of Pakistan.