Enzymes – Chap 7 – Biology MDCAT
Enzymes:
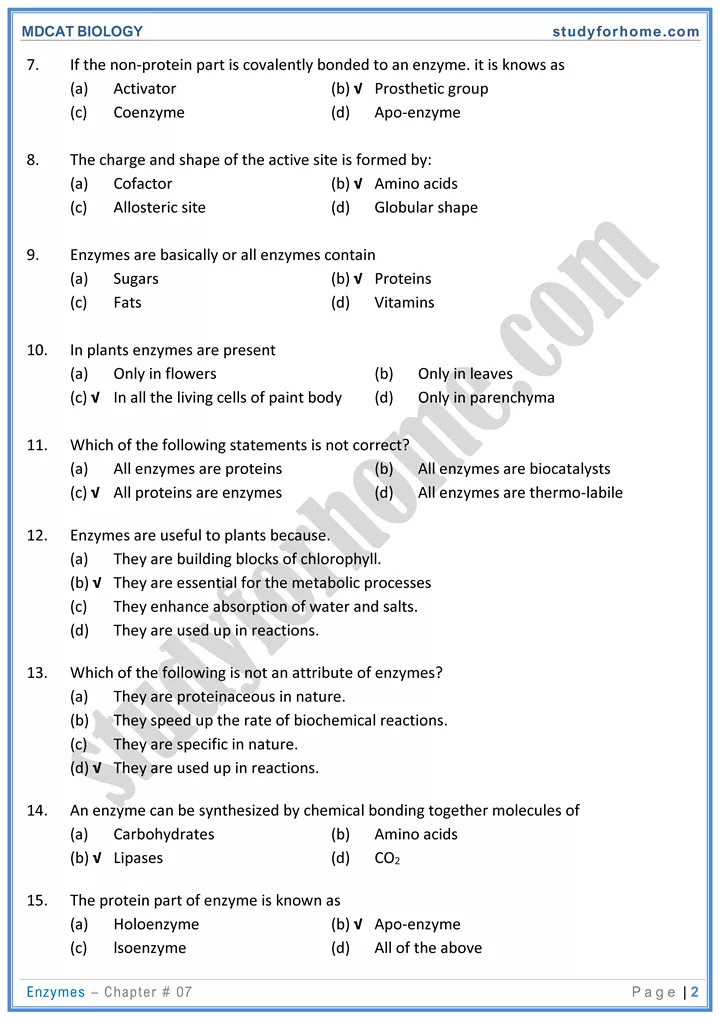
Enzymes are biological catalysts that enhance efficiency of biochemical reactions decreasing energy of activation. Most enzymes are proteinaceous with a few nucleic acids acting as an enzyme.
Characteristics of enzymes:
- Each enzyme is specific for a reaction and works at specific temperature, pH, type of substrate.
- Some enzymes require cofactor for their proper functioning
- They never used up in a chemical reaction.
Types of enzymes:
- Simple enzyme (protoenzyme): Consists of only protein part. e.g. amylase, pepsin.
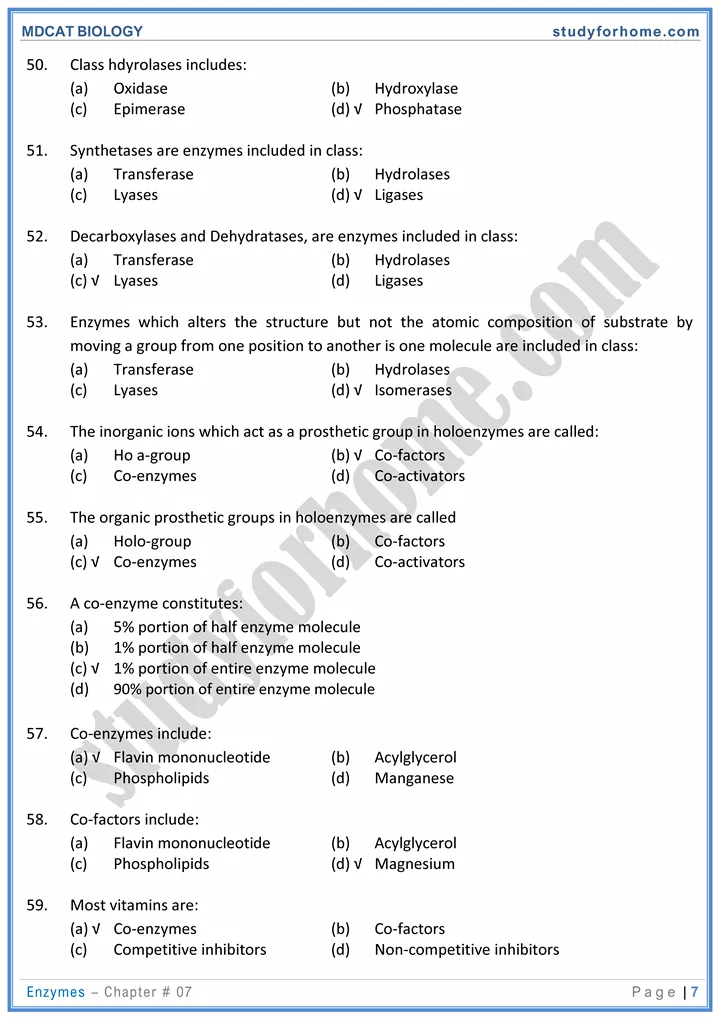
- Conjugated enzyme: Enzyme which consists of protein and a non-protein part is called conjugate enzyme. Holoenzyme is a unit of conjugate enzyme that shows complete activity.
Mode of Action of Enzymes:
- Active site a small part of the enzyme having specific shape and charge. All the substrate binds to this site. There are two models which explain mode of action of enzymes
- Lock and key mode!: According to it enzymes have specific geometric shape and distribution of changes complimentary to substrate.
- Induce fit model: Enzyme’s active site is straightly flexible when a substrate binds to it, the binding cause active site to change its shape to fit the substrate.
Factors Affecting Enzyme Action:
1. Substrate concentration
- The rate of enzymatic reaction is directly proportional to the substrate concentration upto certain Limit. Beyond that limit no significant change occur due to saturation of active sites. Thus more enzyme would be needed to increase the rate.
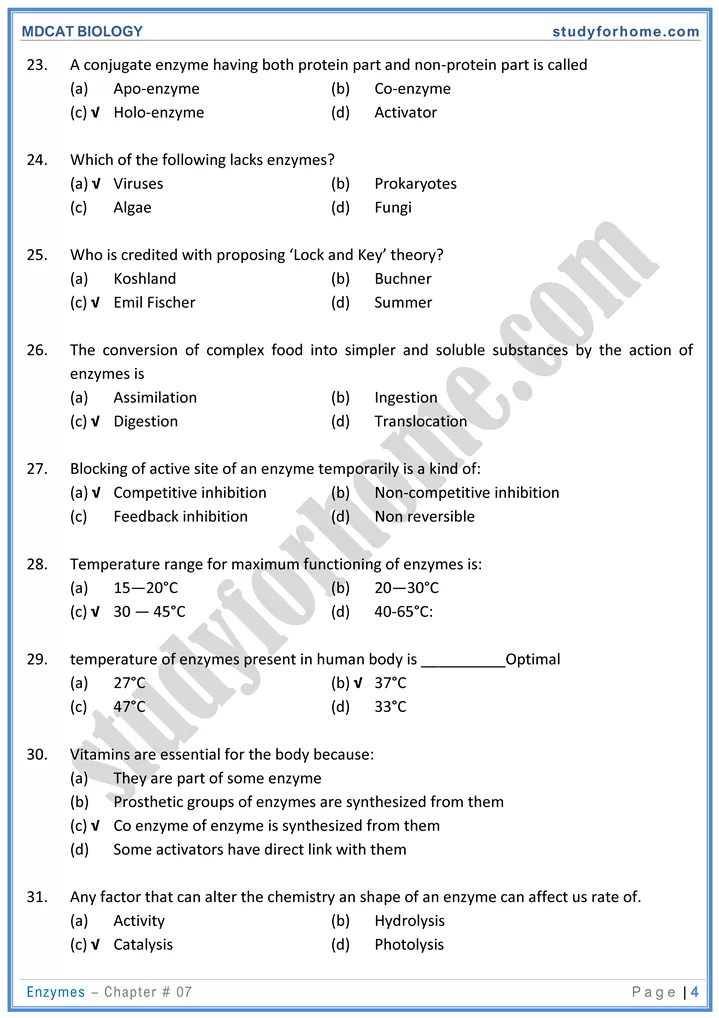
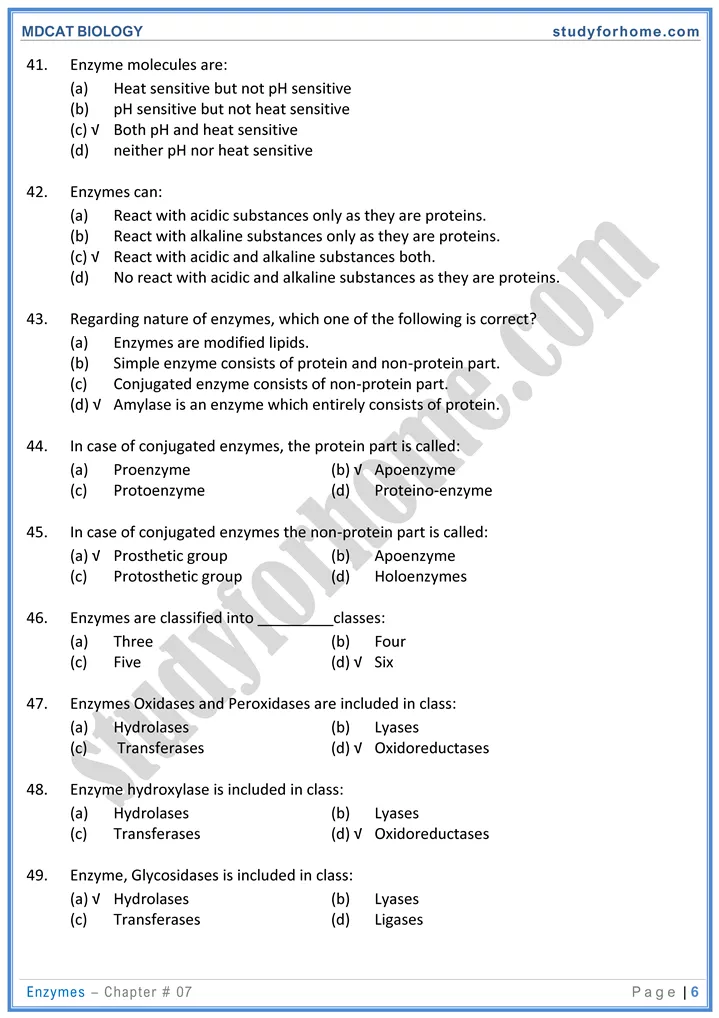
2. Temperature
- Enzymes are inactivated at 0°C denatured at 100°C. The temperature at which maximum activity of enzymes are achieved is called optimum temperature. 37°C is optimum for many enzymes in human body.
3. pH:
- changes in pH of medium influence shape of enzymes and affects its activity. If an enzyme like pepsin has pH range between. 1.4—2.4 is allowed to work in neutral or alkaline medium, it would be inactivated.
4. Coenzymes and activators:
- Some non-protein substances enhance activity of enzymes are called cofactors. If they are inorganic, they are called as activators. If cofactor is organic then it is called as coenzyme.
5. Enzyme inhibitors:
- Substances that decrease enzymatic activity are called inhibitors. They are of following types.
- Competitive inhibitors:-Substances that compete substrate molecules at active site are called competitive inhibitors competitive inhibiton can be reversed by increasing substrate concentrations.
- Non-competitive inhibitors:- Inhibitors that bind to the allosteric site of an enzyme and brings a change in the shape of the enzyme are called non-competitive inhibitors:
- Feedback inhibition:-lf the inhibitor substance is the product of an enzymatic reaction. The product inhibit enzymes activity by binding to its active or allosteric site.
Negative feedback inhibition:
- Most of the biological processes are regulated through this mechanism- In this mechanism if the required product is formed, then the product binds to the enzyme at any place to stop further production.
Sites of Enzymes:
- Many enzymes are present only in cytoplasm e.g enzymes of glycolysis, etc.
- Some enzymes are integral part of ribosomes.
- Enzymes responsible for cellular respiration are present in mitochondria. Enzyme responsible for transcription, replication etc are present in nucleus.
Types of inhibitor:
There are two types of inhibitor
- competitive inhibitor (It is bind with active side of an enzyme it is also called blockers)
- non competitive inhibitor (It is bind with allosteric side of an enzyme it is also called slower)